
- Ping transmit failure but loopback works drivers#
- Ping transmit failure but loopback works software#
Since then, several variants of the ping command have been created and implemented. The original version of the ping was written in 1983 by Mike Muuss at the University of California at Berkeley. A successful ping means that both hosts have proper connectivity and if the path has any routers, they are also running fine. If the source receives the reply datagram, it is considered a successful ping. Reply datagram follows the same steps and procedure to reach the source host. If ICMP and IP modules on the destination host are working properly, the destination host creates a reply datagram and sends it back to the source host. Finally, the destination host receives the datagram. If the path contains multiple intermediate routers, they all use their routing logic to forward the datagram to the destination. The default router uses its routing table to find a path to the destination. If the default router is connected, it forwards the datagram to the default router. If the forwarding table does not contain an entry for the destination, it uses ARP (on IPv4) or Neighbor Discovery (on IPv6) to locate the default router.

If the forwarding table has an entry for the destination device, it forwards the datagram to the destination. If the datagram is correct, it checks an entry in its forwarding table for the destination.
Ping transmit failure but loopback works software#
The ping application creates an IP datagram and gives it to the IP software of the source computer.
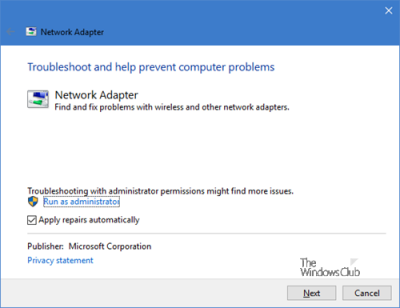
On the source device, a user specifies a ping destination. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) How does the ping command work? (The default setting is 1 second, expressed as 1000 milliseconds.To learn the ICMP protocol and its messages in detail, you can check the following tutorial. For example, the command ping -w 2000 172.16.48.10 waits 2 seconds before timing out. You can use the -w switch to specify a longer time-out. Note If the remote system being pinged is across a high-delay link such as a satellite link, responses might take longer to be returned. Tracert is described in more detail in the following section. Tracert reveals breaks in connectivity but does not provide statistics about router performance. Note To perform this last step more quickly, you can substitute the Tracert utility for the PathPing utility. For troubleshooting purposes, make sure only one default gateway is configured. ■ A default gateway is configured and the link between the host and the default gateway is operational. ■ The local computer's IP address and subnet mask are correctly configured. If you cannot ping successfully at any point, check to make sure the following are true: Ping uses host name resolution to resolve a computer name to an IP address, so if pinging succeeds by address, but fails by name, the problem lies in host name resolution, not network connectivity. To perform this step, enter pathping at a command prompt. Run a PathPing analysis to a remote host to determine which (if any) routers on the way to the destination are malfunctioning. To perform this step, enter ping at a command prompt.Ħ. Ping the host name of a remote host to verify that you can resolve remote host names. To perform this step, enter ping at a command prompt.ĥ. This step verifies that you can communicate with hosts outside your local network segment. Ping the IP address of a remote host located beyond the default gateway. To perform this step, enter ping at a command prompt.Ĥ. This step verifies that the default gateway is reachable and that the local host can communicate with another host on the network. Ping the IP address of the default gateway. To perform this step, enter ping at a command prompt.ģ. Ping the IP address of the local computer to verify that an address has been added correctly.
Ping transmit failure but loopback works drivers#
This problem might be occurring because the TCP drivers are corrupted, the network adapter might not be working, or another service might be interfering with IP.Ģ. If the loopback step fails, the IP stack is not responding. To perform this step, enter ping 127.0.0.1 at a command prompt. Ping the loopback address to verify that TCP/IP is installed and configured correctly on the local computer.


If Network Diagnostics reports that this self-ping test has failed, you can perform the first step manually.)ġ. ( Network Diagnostics automatically performs only the second step. Note The first two steps of the following sequence are already performed by the Ipconfig /all command and Netdiag. When troubleshooting network connectivity, use the Ping command to perform the following sequence of tasks. You can also use the Ping tool to locate remote hardware problems and incompatible configurations. Use Ping whenever you want to verify that a host computer can send IP packets to a destination host. When troubleshooting, the Ping command is used to send an ICMP echo request to a target host name or IP address. Ping is a tool that helps to verify IP-level connectivity PathPing is a tool that detects packet loss over multiple-hop trips.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
